In recent years, the construction industry has witnessed a groundbreaking technological advancement known as 3D construction printing, revolutionizing the way buildings and structures are created. This innovative approach combines 3D printing technology with construction, offering numerous benefits in terms of speed, cost-efficiency, and design flexibility. In this introduction, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts and key aspects of 3D construction printing.
What Is 3D Construction Printing?
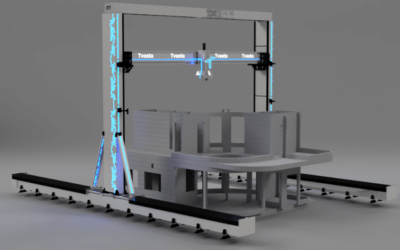
3D construction printing, also known as 3D concrete printing or additive construction, is a revolutionary construction method that involves the use of large-scale 3D printers to create three-dimensional structures layer by layer. Instead of traditional construction methods that rely on manual labor and the assembly of individual building components, 3D construction printing automates the construction process by depositing layers of construction material, typically concrete, in a precise and controlled manner.
How Does 3D Construction Printing Work?
The process of 3D construction printing typically involves the following steps:
- Digital Design: An architectural design or 3D model of the structure is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This digital model serves as the blueprint for the 3D printer.
- Material Preparation: Specialized construction materials, such as 3D printable concrete, are mixed and prepared for use in the 3D printer. These materials are formulated to meet structural and durability requirements.
- Printing Process: The 3D printer, equipped with a nozzle or extrusion system, follows the digital model’s instructions to deposit layers of construction material. The layers are typically laid down in a zigzag or grid pattern, gradually building up the structure.
- Layer-by-Layer Construction: The 3D printer continues to add layers, with each layer bonding to the previous one through a combination of chemical reactions and mechanical bonding. This layer-by-layer approach allows for precise control over the structure’s geometry.
- Curing and Finishing: After the printing process is complete, the structure may undergo curing to strengthen the material. Additional finishing work, such as smoothing or surface treatments, may also be applied.
Benefits of 3D Construction Printing:
3D construction printing offers several advantages over traditional construction methods:
- Speed: The automated nature of 3D printing allows for significantly faster construction, reducing project timelines.
- Cost-Efficiency: Lower labor costs and reduced material waste contribute to cost savings.
- Complex Geometry: 3D printing enables the creation of complex architectural designs that are challenging to achieve with traditional methods.
- Sustainability: Reduced material waste and the ability to use eco-friendly construction materials make 3D printing a sustainable option.
- Customization: Structures can be customized easily, making it suitable for unique and bespoke designs.
Applications of 3D Construction Printing:
3D construction printing has a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential housing
- Commercial buildings
- Bridges and infrastructure
- Disaster relief housing
- Cultural and art installations
As 3D construction printing continues to advance, its potential applications and impact on the construction industry are expected to grow significantly.
In conclusion, 3D construction printing represents a transformative technology with the potential to reshape the construction industry by offering speed, cost-efficiency, and design flexibility. As the technology evolves, it is likely to play a crucial role in addressing housing challenges, promoting sustainability, and enabling innovative architectural designs.